Tourism multiplier effect
The concept of tourism multiplier effect has been gaining traction in recent years. Certainly, the tourism industry has a multiplier effect that extends beyond the direct spending by tourists. This multiplier effect creates jobs, stimulates economic growth, and promotes community development.
What is the tourism multiplier effect?
The tourism multiplier effect refers to how many times the money spent by a tourist circulates in the country’s economy (Byju’s, 2023). Broadly, it refers to the economic impact of tourism that extends beyond the initial spending by visitors.
When tourists spend money, it creates a ripple effect that stimulates economic activity in various sectors. This multiplier effect can be quantified by measuring the direct and indirect effects of tourism on the economy.
The multiplier effect occurs because the money spent by tourists does not only benefit the businesses that directly serve tourists, but also spreads throughout the local economy. This effect can be seen in a wide range of industries, including transportation, accommodation, food and beverage, and retail.
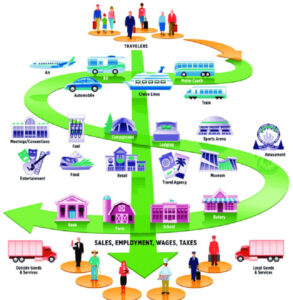
The tourism multiplier effect is especially important for countries that rely heavily on tourism as a source of revenue. For example, tourism accounts for more than 28% of the GDP of Maldives (Michigan State University, 2023).
Likewise, tourism and related services contribute approximately 70 percent to the GDP of Bahamas and employs over half of the workforce (ITA, 2022). Therefore, understanding the tourism multiplier effect is essential for policymakers and stakeholders in the tourism industry.
Types of tourism multipliers
There are two types of tourism multipliers: direct and indirect. Direct multipliers refer to the initial spending by visitors, such as accommodation, food, and transportation. Indirect multipliers refer to the subsequent spending by businesses that supply goods and services to the tourism industry.
For example, a hotel that purchases food from a local supplier creates indirect economic activity for the supplier. The local suppliers that provide food to hotels and restaurants may experience an increase in sales during peak tourism season, which can lead to the hiring of additional staff and a boost in tax revenue for the local government.
The tourism multiplier effect also creates induced multipliers, which refer to the spending by employees and business owners who benefit from the direct and indirect effects of tourism. For example, a hotel employee who earns a salary spends money on goods and services, which creates additional economic activities.
The economic effects of tourism on local businesses
The tourism industry can have a significant impact on local businesses. When tourists spend money on goods and services, it creates income for local businesses. This income can be reinvested in the local economy, creating a multiplier effect that stimulates economic growth.
However, the tourism industry can also have negative effects on local businesses. For example, if a large hotel chain opens in a small town, it can put small local hotels out of business. Therefore, policymakers must balance the benefits and costs of tourism to ensure that local businesses are not negatively impacted.
Jobs created by the tourism industry
The tourism industry is a significant source of employment for many countries. In some countries, such as Maldives and Bahamas, it is indeed the primary source of employment.
The jobs created by the tourism industry can vary from low-skilled to high-skilled positions, such as tour guides, hotel managers, and chefs. These jobs provide opportunities for people with different levels of education and skills.
The number of jobs created by tourism depends on the level and type of activities. For example, a large-scale resort may create thousands of jobs, while a small bed and breakfast may only create a few jobs.
The total number of tourism employees in the USA is around 6 million (IBISWorld, 2023). Tourism supports around 3.8 million jobs in the UK. Just imagine the impact of the spending of all these people on the economy!
Community development from tourism
Tourism can promote community development by generating income and creating jobs. This income can be used to improve infrastructure, support local businesses, and invest in community projects.
For example, a city that attracts a large number of tourists may use the tax revenue generated by tourism to improve public transportation or build new community facilities.
Tourism can also have a cultural impact on local communities. It can promote cultural exchange and understanding, as tourists learn about local customs and traditions. This can help to preserve and promote local culture, which can have a positive impact on the community.
Environmental impact of tourism
Tourism can have a positive environmental impact. It can promote conservation and the protection of natural resources. For example, a national park that attracts tourists may receive funding for conservation efforts, which can help to preserve the park’s ecosystem.
However, tourism can also have a negative impact on the environment. The construction of new hotels and resorts can lead to deforestation, habitat destruction, and pollution. Tourists can also contribute to environmental degradation by generating waste and consuming natural resources.
Therefore, the tourism industry must adopt sustainable practices to minimize its impact on the environment. This includes reducing waste, conserving energy, and protecting natural habitats.
How to measure the tourism multiplier effect?
Measuring the tourism multiplier effect can be challenging because it involves the analysis of multiple factors. However, there are several methods that can be used to measure the effect, including input-output analysis, employment multipliers, and value-added multipliers.
Input-output analysis involves examining the flow of money through the local economy. This analysis can be used to determine the direct and indirect impacts of tourism spending on local businesses.
Employment multipliers measure the number of jobs created by a given level of tourism spending. This method can be used to estimate the employment impact of tourism in a particular area.
Value-added multipliers measure the additional income generated by a given level of tourism spending. This method can be used to estimate the overall economic impact of tourism in a particular area.
Examples of successful tourism multiplier effect in different countries
Many countries and regions have successfully harnessed the power of the tourism multiplier effect to stimulate economic growth and promote community development. For example, tourism and the night-time economy contribute £36 billion a year to London’s economy overall and employ 700,000 people (Greater London Authority, 2023).
The tourism industry has been a significant contributor to the economic growth of the USA. It has created jobs and stimulated economic activities in various sectors, such as agriculture, transportation, and retail. It has contributed nearly $1.3 trillion to the GDP (Statista, 2022). It indeed supports millions of American jobs.
The tourism industry contributes around19.96 billion Canadian dollars to Canada’s GDP. Likewise, Australia’s direct tourism gross domestic product reached around 35.14 billion Australian dollars in 2022.
Costa Rica has developed a sustainable tourism industry that promotes conservation and community development. Its tourism industry generates significant income and employment opportunities, while also protecting its natural resources.
Similarly, Iceland has developed a tourism industry that promotes its unique natural features, such as geysers, glaciers, and hot springs. Its tourism industry has created jobs and generated income, while also promoting sustainable tourism practices.
Limitations of the tourism multipliers
One of the key challenges concerning tourism is economic leakage. It occurs when international companies provide hotel, flight, car hire, food, and excursions at a destination and a lot of money generated from these activities goes out of the destination to the country whether their headquarters are located.
Faith (2023) reports that 80% of the revenue generated from tourism activities go away from the local communities to foreign countries. This shows how the local communities that are supposed to benefit from the tourism multiplier effects are not benefiting optimally.
Conclusion: Tourism multiplier effect
In conclusion, the tourism multiplier effect is a powerful force that can drive economic growth and promote community development. By understanding its various components and adopting sustainable practices, the tourism industry can unlock its full potential and create a better future for all. However, it is also important to recognise the potential negative impacts of tourism and explore steps to mitigate them.
To harness the power of the tourism multiplier effect, the tourism industry must adopt sustainable practices that minimize its impact on the environment. The industry must also promote cultural exchange and preserve local traditions and heritage.
Hope you like this article? Please share the article link on social media to support our work. You may also like the following articles:
Enclave tourism – definition and characteristics
Advantages and disadvantages of eco-tourism
Last update: 03 April 2023
References:
Byju’s, (2023) What is the tourism multiplier effect? Available at: https://byjus.com/ias-questions/what-is-the-tourism-multiplier-effect/ (accessed 02 April 2023)
Faith, S. (2023) Tourism’s dirty secret, available at: https://www.euronews.com/travel/2023/02/26/tourisms-dirty-secret-what-is-tourism-leakage-and-how-can-you-avoid-contributing-to-it (accessed 01 April 2023)
Greater London Authority (2023) Supporting the tourism sector, available at: https://www.london.gov.uk/programmes-strategies/business-and-economy/supporting-londons-sectors/supporting-tourism-sector (accessed 02 April 2023)
IBISWorld (2023) Tourism in the USA, https://www.ibisworld.com/industry-statistics/employment/tourism-united-states/ (accessed 02 April 2023)
ITA (2022) Bahamas- the country economic guide, available at: https://www.trade.gov/country-commercial-guides/bahamas-market-overview# (accessed 03 April 2023)
Michigan State University (2023) Maldives economy, available at: https://globaledge.msu.edu/countries/maldives/economy (accessed 03 April 2023)
Statista (2022) Total contribution of travel and tourism to the gross domestic product in the United States, available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/292518/contribution-of-travel-and-tourism-to-gdp-in-us-time-series/ (accessed 03 April 2023)
Photo credit: Research Gate/Travel and Tourism
Author: M Rahman
M Rahman writes extensively online and offline with an emphasis on business management, marketing, and tourism. He is a lecturer in Management and Marketing. He holds an MSc in Tourism & Hospitality from the University of Sunderland. Also, graduated from Leeds Metropolitan University with a BA in Business & Management Studies and completed a DTLLS (Diploma in Teaching in the Life-Long Learning Sector) from London South Bank University.



